Computer Studies Notes Form 4
Computer Studies Notes Form 4
Introduction to Networking and Data Communication
Welcome!
Computers communicate to one another; however they should be interconnected (networked) in order for communication to take place.
The best example where computers communicate to one another is through Internet or usage of mobile phones.
A number of procedures and elements are needed in order for communication to take place. In this tutorial, we are going to learn the following topics:
1. Definition of terms used in networking
2. Types of computer networks
3. Purpose and demerits of networking
4. Elements of networking
5. Network topologies and
6. Network security
At the end of this topic therefore, you should accomplish the tasks listed above and be able to attempt assessments to clarify you understanding on logic
1.2 Definition of Terms Used in Networking
Definition of Terms Used in Networking
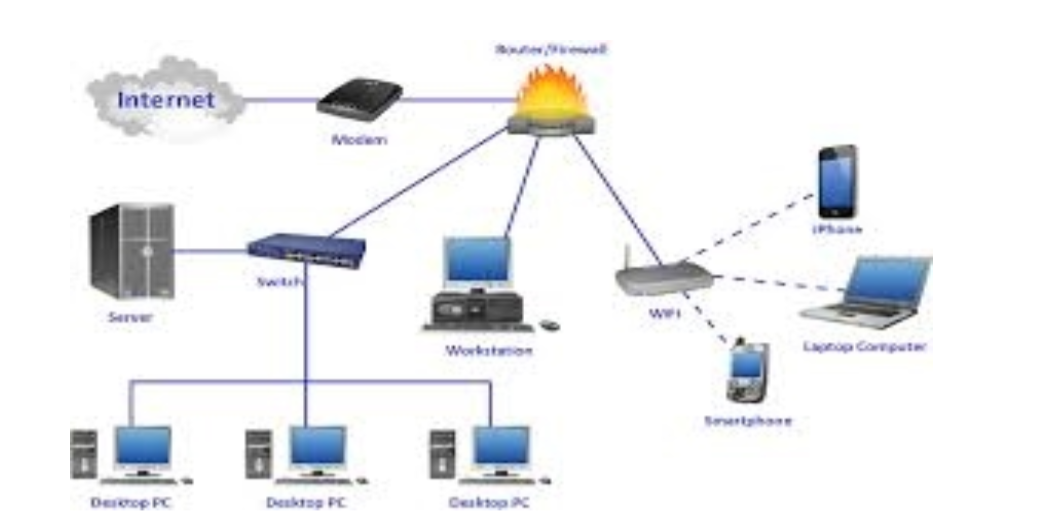
Network A network is the infrastructure that supports electronic data exchange.Either, it can be defined as a collection of independent entities that are arranged to exchange data or resources
Computer Network
A computer network therefore can be defined as a collection of computers linked together using transmission media for the purpose of communication and resource sharing.
Transmission Media
This is any physical or non-physical link between two or more computers and in which a signal can be made to flow from source to destination.
These shared resources include:- application programs, printers, fax machines, modems, storage devices etc.
Data Communication
Data communication is a process of transmitting data signals from one point to another through the network.
Data Signal
A data signal is a voltage level in the circuit which represents the flow of data. data signal can either be digital or analogue
Modulation
This is a process by which the characteristics of electrical signals are transformed to represent information.
Types of modulation include AM, FM, and PAM.i.e converting digital signal to analogue
Demodulation
This is a process of returning a modulated signal to its original form.
Modems perform demodulation by taking an analog signal and returning it to its original (digital) form.
Multiplexing
This is the process of sending multiple data signals over the same medium
Demultiplexing
This is the process of separating the multiplexed signals at the receiving end Bandwidth
This is the maximum amount of data that a transmission medium can carry at lany one time Baseband Signal
This is a digital signal that is generated and applied tot he transmission medium directly without modulation
Broadband Transmission
An analogue signal is sent over the transmission medium using a particular frequency
Attenuation
This is a decrease in magnitude and energy as a signal progressively moves along a transmission medium
Repeater
A Physical Layer device which restores, amplifies, re-clocks or otherwise improves a network signal that it receives on one of its ports and transmits the improved signal without buffering or interpreting it.
Modes of data communication
Simplex
This is communication in only one direction e.g. radio broadcasting
Half Duplex
Refers to communication in both directions but one direction at a time e.g. using a walkie talkie
Full Duplex
This is communication that occurs in both directions simultaneously
1.3 Computer Network and Types
Computer Network
1. A computer network or data network is a telecommunications network that allows computers to exchange data.
Types of computer networks
There are different types of networks. Namely: Personal Area Network (PAN), Local Area Network (LAN), Metropolitan Area Network (MAN), Wide Area Network (WAN) and Internetwork
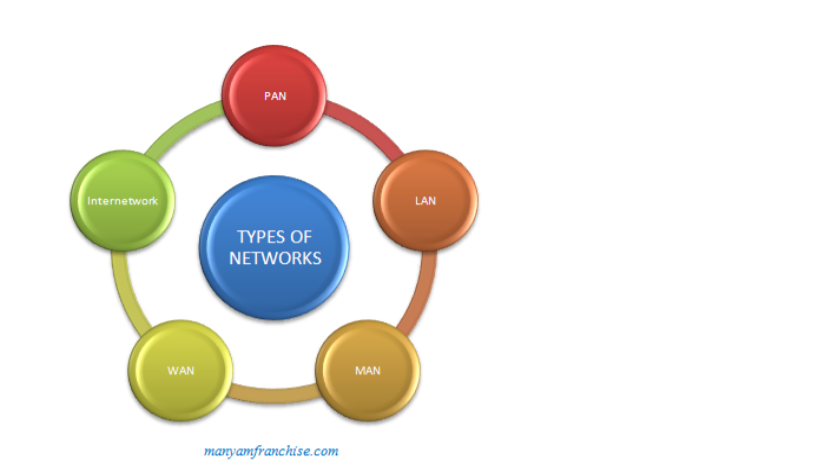
Note: KCSE Syllabus limits types of networks as LAN, MAN and WAN (students should stick with the syllabus)
Personal Area Network
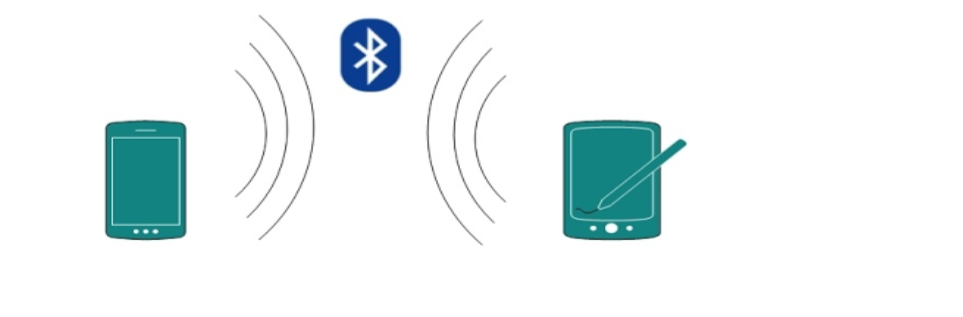
A Personal Area Network or simply PAN, is smallest network which is very personal to a user.
This may include Bluetooth enabled devices or infra-red enabled devices. PAN has connectivity range up to 10 meters.
PAN may include wireless computer keyboard and mouse, Bluetooth enabled headphones, wireless printers and TV remotes for example.
Piconet is an example Bluetooth enabled Personal Area Network which may contain up to 8 devices connected together in a master-slave fashion.
Local Area Network
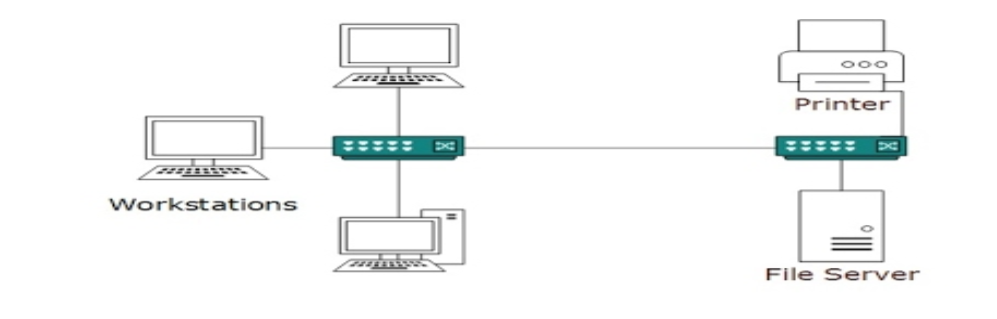
A computer network spanned inside a building and operated under single administrative system is generally termed as Local Area Network. Usually, Local Area Network covers an organization’s offices, schools, college/universities etc.
Number of systems may vary from as least as two to as much as 16 million.
LAN provides a useful way of sharing resources between end users.
Resources like Printers, File Servers, Scanners and internet is easy sharable among computers.
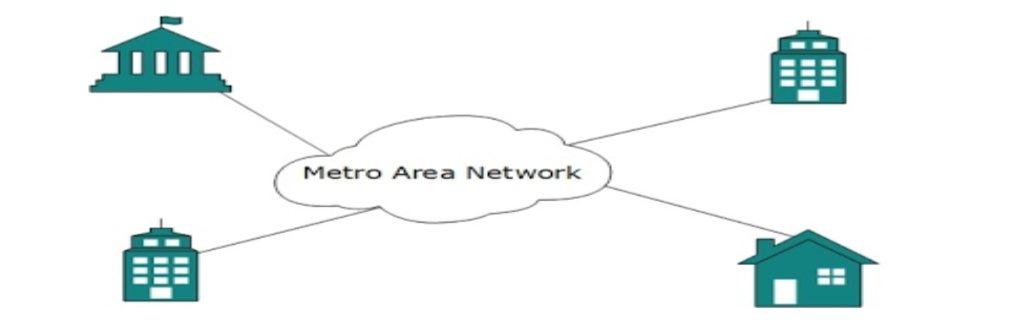
Metropolitan Area Network
MAN, generally expands throughout a city such as cable TV network.
It can be in form of Ethernet, Token-ring, ATM or FDDI.
Metro Ethernet is a service which is provided by ISPs.
This service enables its users to expand their Local Area Networks. For example, MAN can help an organization to connect all of its offices in a City.
Backbone of MAN is high-capacity and high-speed fiber optics. MAN is works in between Local Area Network and Wide Area Network. MAN provides uplink for LANs to WANs or Internet.
Wide Area Network
As name suggests, this network covers a wide area which may span across provinces and even a whole country. Generally, telecommunication networks are Wide Area Network.
These networks provides connectivity to MANs and LANs.

Internetwork
A network of networks is called internetwork, or simply Internet. It is the largest network in existence on this planet. Internet hugely connects all WANs and it can have connection to LANs and Home networks.
Internet enables its users to share and access enormous amount of information worldwide.
It uses www, ftp, email services, audio and video streaming etc. At huge level, internet works on Client-Server model.
Internet uses very high speed backbone of fiber optics.
To inter-connect various continents, fibers are laid under sea known to us as submarine communication cable.
Internet is widely deployed on World Wide Web services using HTML linked pages and is accessible by some client software known as Web Browsers.
When a user requests a page using some web browser located on some Web Server anywhere in the world, the Web Server responds with the proper HTML page. The communication delay is very low.
Internet is serving many proposes and is involved in many aspects of life.
Some of them are:
• Web sites
• Instant Messaging
• Blogging
• Social Media
• Marketing
• Networking
• Resource Sharing
• Audio and Video Streaming
2024 FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION RESOURCES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 OPENER , MID AND END TERM EXAMS
1995-2024 KCSE KNEC PAPERS QUESTIONS,ANSWERS AND REPORT
2008-2024 KCSE FORM 4 COUNTY MOCKS
FORM 1 2 3 4 SCHEMES OF WORK
FORM 1 2 3 4 LESSON PLANS
FORM 1 2 3 4 CLASS REVISION NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 HOLIDAY ASSISNMENTS
FORM 3 4 SETBOOKS STUDY GUIDES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TOPICAL TESTS
FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION BOOKLETS
LIFE SKILLS NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 SYLLABUS
KENYA SCHOOL CODES
HOW TO REVISE AND PASS EXAMS
GUIDANCE AND CONSELLING NOTES
 WhatsApp us Now
WhatsApp us Now