Computer Studies Notes Form 2
Computer Studies Notes Form 2
Computer Studies Notes Form 2
Chapter 1 Word Processors
This chapter introduces the student to what Word Processors are, and how they are used.
1.1 Definition of a Word Processor
1.2 Purpose of Word Processing
1.3 Using a Word Processor
1.4 Format and edit a document
1.5 Create and edit a table
1.6 Create and edit a mail merge document
1.7 Print a document
1.8 Insert and edit objects
1.1 Definition of a Word Processor
A Word Processor (WP) is an application or a program (software) that converts letters into words, words into sentences, sentences into paragraph and paragraph into a document for purposes of communication.
This process is known as Word Processing. There are several word processors available for users in the work place and in schools.
Examples include: Ms-Word, Word Perfect, WonderWord, WordPro and so on.
1.2 Features of Word Processors
All word processors possess certain features that are unique to them.
The following are some of the features of WP.
1. Cursor – all WP possess a blinking cursor that shows the user where next to type. You can only be able to type exactly at the position of the cursor. Once you type, the cursor then moves to the next available space.
2. Formatting and Editing -Formatting is changing the appearance of text by selecting font typeface or hand writing style), colour, alignment, indentation (moving text away from the margins), bolding, changing size, underline, italic and making bulleted list.
Editing is correcting errors and ensuring clarity and accuracy like removing spelling and grammar mistakes.
3. Spelling and grammar check – WPs have the ability to check the spelling and the grammar of a document.
This can be set to indicate such mistakes by showing different colours on them. For example in Ms-Word, spelling mistakes are underlined in red and grammar are underlined in green.
The user then has the chance to correct the mistakes either immediately or after completing the task being done. Refer to section 1.5 for details.
4.Word Wrap– WPs have the ability to take an incomplete word to the next line automatically without pressing the enter key.
This is known as word wrap.
5. Thesauras – this is a Greek word for storehouse. It stores synonyms and antonyms of different words. The user of the WP has the option to obtain different words which mean the same or opposite as the word to be changed.
6. Auto-correct – word which is frequently used with WP can be made to automatically be corrected or be completed by WP in the process of typing, hence the name auto-correct. Refer to section 1.4 for details.
7. Undo and redo – any action done by the user of the WP, can be undone by these two features. If the user types some words which was not intended, one has the option to click undo button for the action to be omitted or if one had deleted some word or sentence or paragraph by mistake, one simply presses the redo button to have the same deleted items back to the right place.
8. Mail Merge – this is the ability of WP to create a common letter, e-mail or labels and add different addresses or particulars to each letter for different people at the same time.
It has three main parts: creating main letter, creating addresses and merging the addresses to the letter. Refer to section 1.7 for details.
9. Dictionary – WP has a dictionary where certain words can be added, to make them accepted by WP such that it will not show the red colour symbolizing that it is a spelling mistake or a non English word.
You can add nouns from a different language and WP will recognize them as part of the English language. Depending on the default language used by the computer, certain words may not be accepted though they are English words. You need to add such words to the dictionary of WP. For example, British English will accept labour, but American will only accept labor and so on.
1.3 Purpose of a Word Processor
The purpose of a WP from the definition above is to create documents for purposes of communication.
The essence of any word processing is to enable messages to be created for onward transmission to the reader.
Such documents in the work place include letters, reports, circulars, emails, newsletters, memos and so on. The documents can then be printed, or conveyed through other means such as e-mails, or through facsimile (fax).
1.4 Using a Word Processing Package
1.4.1 Getting started
The first thing is to load the WP application you intend to use. The example that follows will make use Microsoft Word (MS-Word) as a platform since most schools and organisations use the same. The operating system under which the MS-Word is running is known as Windows Xp.
• To load the application to the following:
• Click Start button
• Go to All programs
• Click Microsoft office
• Click Microsoft office Word
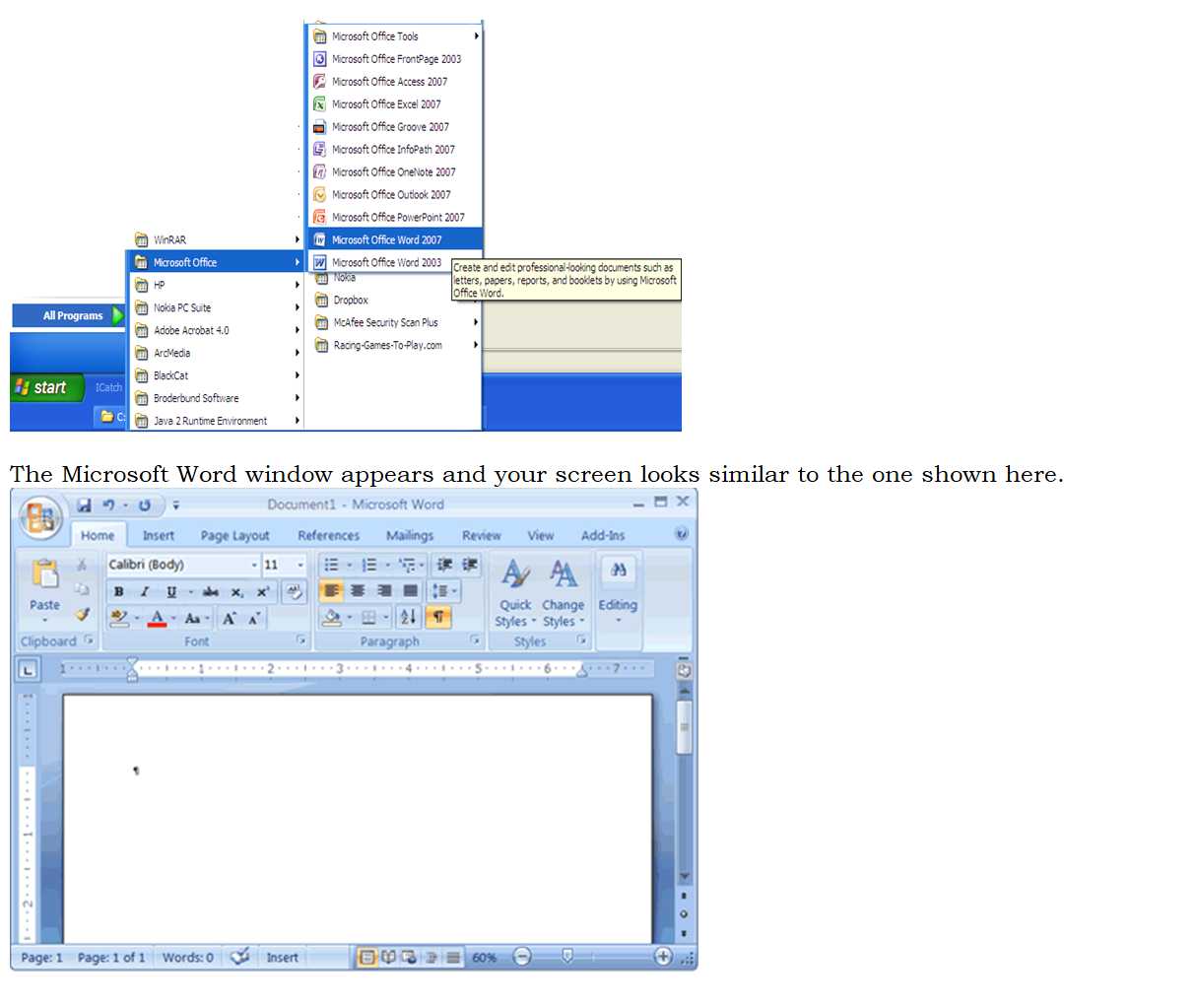
Note: Your screen will probably not look exactly like the screen shown. In Word 2007, how a window displays depends on the size of your window, the size of your monitor, and the resolution to which your monitor is set.
Resolution determines how much information your computer monitor can display. If you use a low resolution, less information fits on your screen, but the size of your text and images are larger.
If you use a high resolution, more information fits on your screen, but the size of the text and images are smaller. Also, Word 2007, Windows Vista, and Windows XP have settings that allow you to change the color and style of your windows.
The Microsoft Office Button
In the upper-left corner of the Word 2007 window is the Microsoft Office button. When you click the button, a menu appears.
You can use the menu to create a new file, open an existing file, save a file, and perform many other tasks.

The Quick Access Toolbar
Next to the Microsoft Office button is the Quick Access toolbar. The Quick Access toolbar provides you with access to commands you frequently use.
By default Save, Undo, and Redo appear on the Quick Access toolbar. You can use Save to save your file, Undo to rollback an action you have taken, and Redo to reapply an action you have rolled back.

The Title Bar
Next to the Quick Access toolbar is the Title bar. The Title bar displays the title of the document on which you are currently working. Word names the first new document you open Documentl. As you open additional new documents, Word names them sequentially. When you save your document, you assign the document a new name.
- Document l – Microsoft WordThe Ribbon
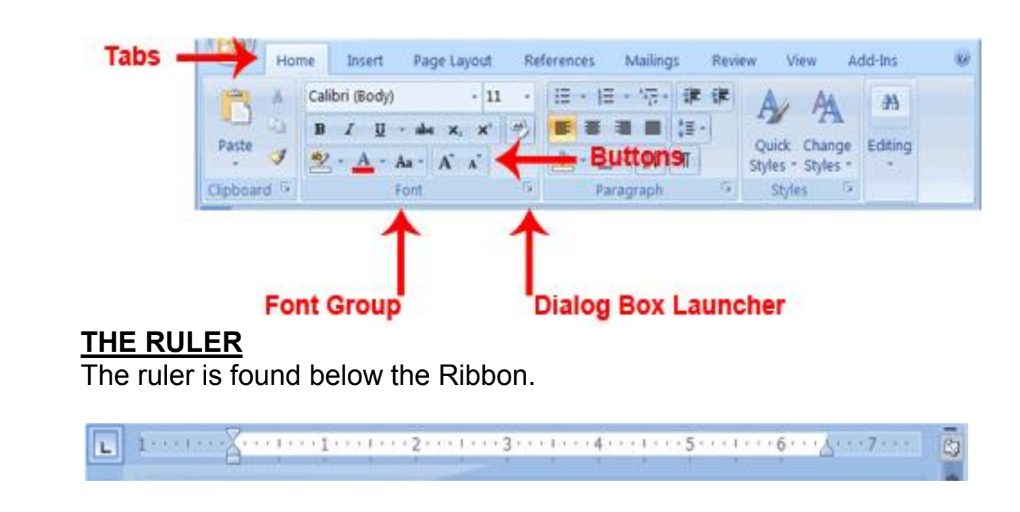
You use commands to tell Microsoft Word what to do. In Microsoft Word 2007, you use the Ribbon to issue commands.
The Ribbon is located near the top of the screen, below the Quick Access toolbar.
At the top of the Ribbon are several tabs; clicking a tab displays several related command groups. Within each group are related command buttons. You click buttons to issue commands or to access menus and dialog boxes.
You may also find a dialog box launcher in the bottom-right corner of a group. Clicking the dialog box launcher gives you access to additional commands via a dialog box.


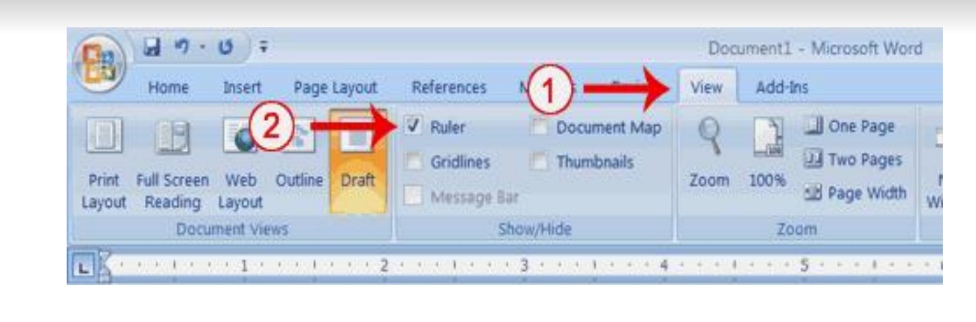
1. Click the View tab to choose it.2. Click the check box next to Ruler in the Show/ Hide group. The ruler appears below the Ribbon.
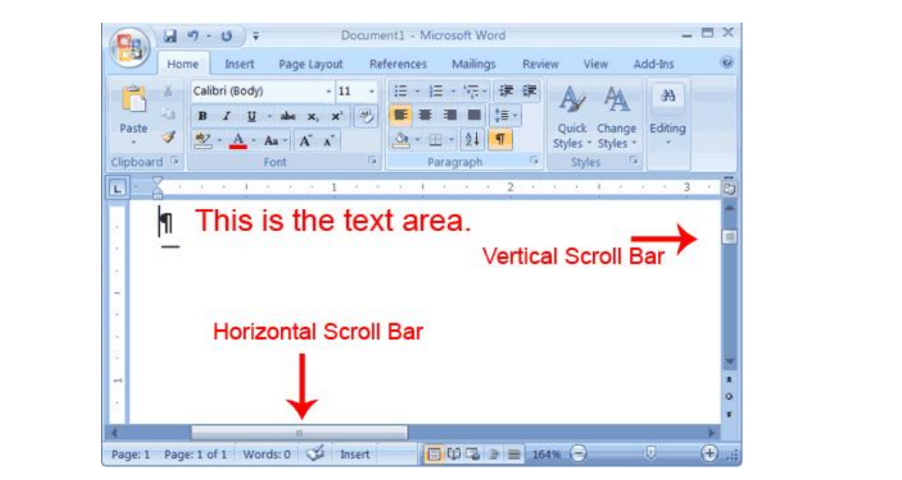
The Text Area
Just below the ruler is a large area called the text area. You type your document in the text area.
The blinking vertical line in the upper-left corner of the text area is the cursor.
It marks the insertion point.
As you type, your text displays at the cursor location. The horizontal line next to the cursor marks the end of the document.

2024 FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION RESOURCES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 OPENER , MID AND END TERM EXAMS
1995-2024 KCSE KNEC PAPERS QUESTIONS,ANSWERS AND REPORT
2008-2024 KCSE FORM 4 COUNTY MOCKS
FORM 1 2 3 4 SCHEMES OF WORK
FORM 1 2 3 4 LESSON PLANS
FORM 1 2 3 4 CLASS REVISION NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 HOLIDAY ASSISNMENTS
FORM 3 4 SETBOOKS STUDY GUIDES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TOPICAL TESTS
FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION BOOKLETS
LIFE SKILLS NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 SYLLABUS
KENYA SCHOOL CODES
HOW TO REVISE AND PASS EXAMS
GUIDANCE AND CONSELLING NOTES
 WhatsApp us Now
WhatsApp us Now