Chemistry Notes Form 4
Chemistry Notes Form 4
Factors that affect the rate of evaporation
Evaporation occurs at all temperatures at the surface of the liquid
It happens more rapidly when:
i) The temperature is higher, since then more molecules in the liquid are moving fast enough to escape from the surface,
ii) The surface area of the liquid is large so giving more molecules a changes to escape because more are near the surface, and
iii) Wind or draught is blowing over the surface carrying vapour molecules away from the surface thus stopping them from returning to the liquid and making it easier for more liquid molecules to break free
Kinetic Theory and Gas Laws
Due to the kinetic theory we begin to understand why gases exert pressure
The molecules of a gas are far apart and in continuous random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the vessel in which the gas is held
The molecules have mass, so they have energy hence they exert force on each collision and hence pressure
If the temperature of the gas is increased at constant volume, the molecules gain more energy and move faster, hitting the walls with more force and exerting greater pressure
If the volume of the gas is increased at constant temperature, the molecules have more space in which to move
The frequency of collisions decreases reducing the pressure
Boyle’s law
The pressure of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its volume if its temperature is kept constant
Consider a gas trapped in a container as shown
The mass, hence number of moles are constant and do not change during the course of the investigation
The piston is frictionless and moves smoothly without allowing the gas to escape
When the pressure changes, the volume of the gas changes as shown
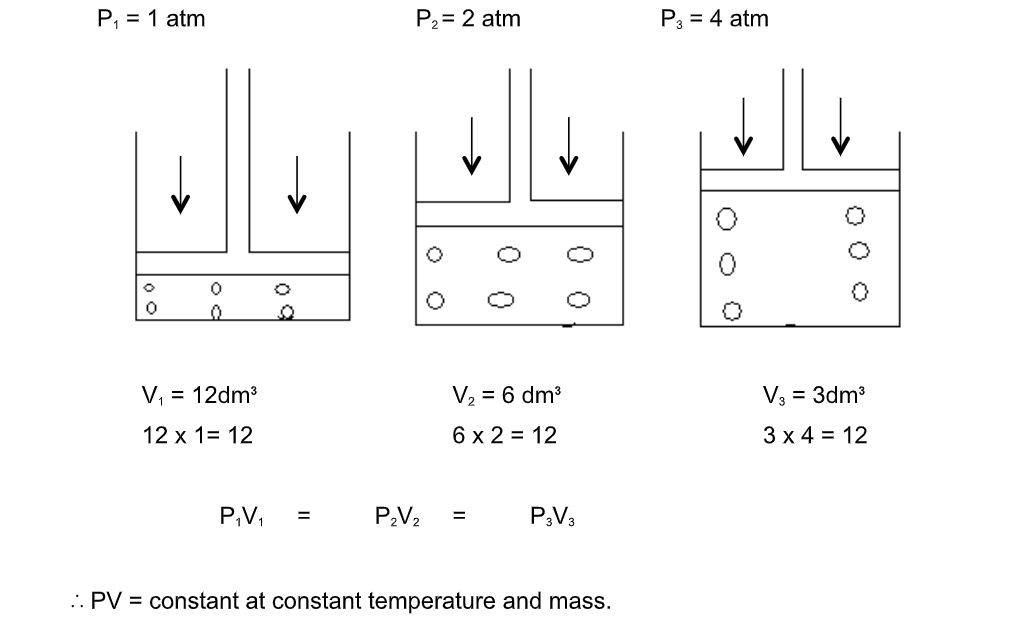
Graphical representation of Boyle’s law
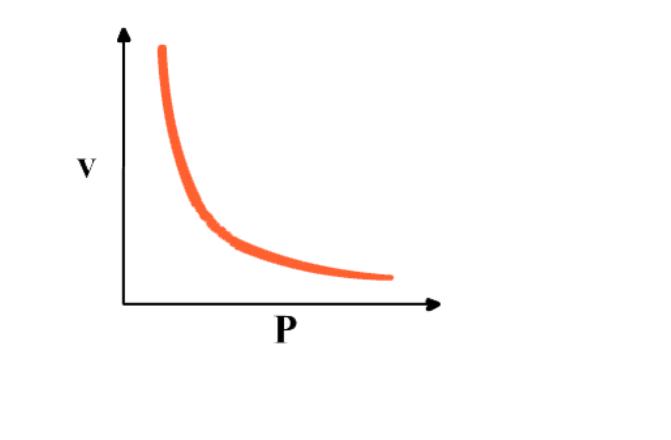
Graph between P & V at constant temperature is a smooth curve known as “parabola”
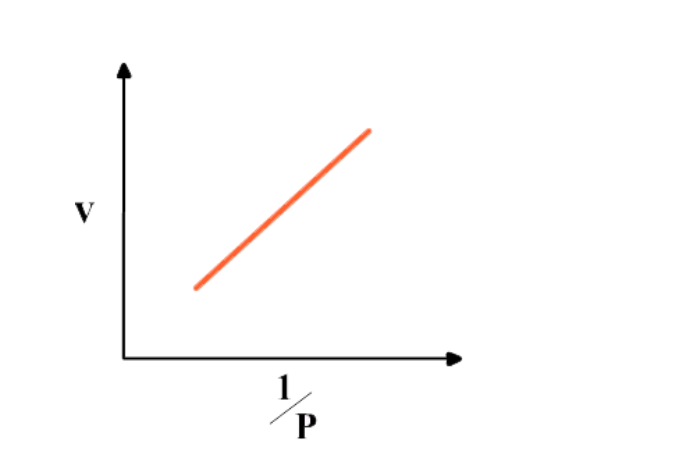
Graph between 1/P & V at constant temperature is a straight line
If pressure, p is doubled, the volume is halved
That is, p is inversely proportional to V
In symbols
P ∝ 1/V or p = constant X 1/V
PV = constant
p1V1 = p2V2 = constant.This is Boyle’s law
Charles’ Law
The volume of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature if the pressure is kept constant
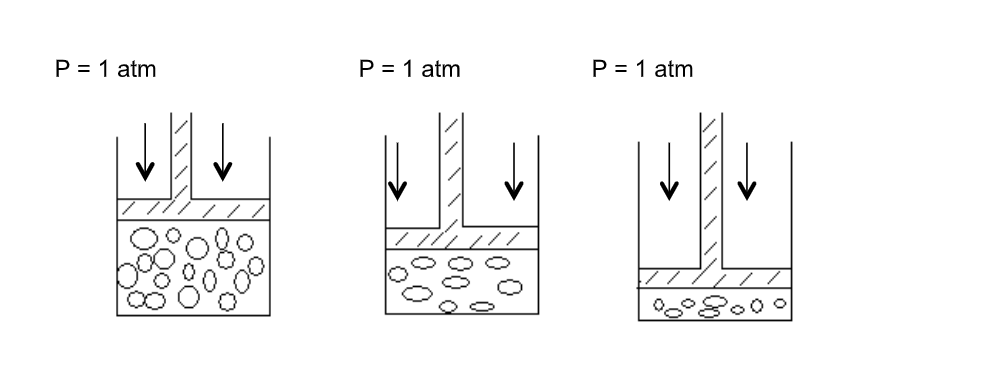
We can then say that the volume V is directly proportional to the absolute temperature T, ie doubling T doubles V, etc Therefore
V ∝ T or V = constant X T
Or V/T = Constant
Volume V1 = 1dm3 V2 = 2dm3 V3= 3 dm3
Temperature (OC) 0 ºC 273 ºC 546 ºC
Temp (K) 273 K 546K 819K
Volume/Temp 1/273 2/546 3/819
Equation ∴ V1/T1 = V2/T2 = V3/T3
∴ V/T = constant
Graphical representation
Graph between Volume and absolute temperature of a gas at constant pressure is a “straight line”
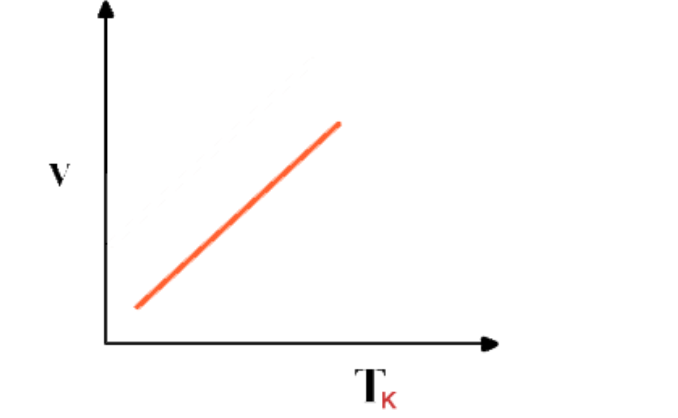
Absolute scale of temperature or absolute zero
If the graph between V and T is extrapolated, it intersects T-axis at -273
16 0C
At -273
16 0C volume of any gas theoretically becomes zero as indicated by the graph
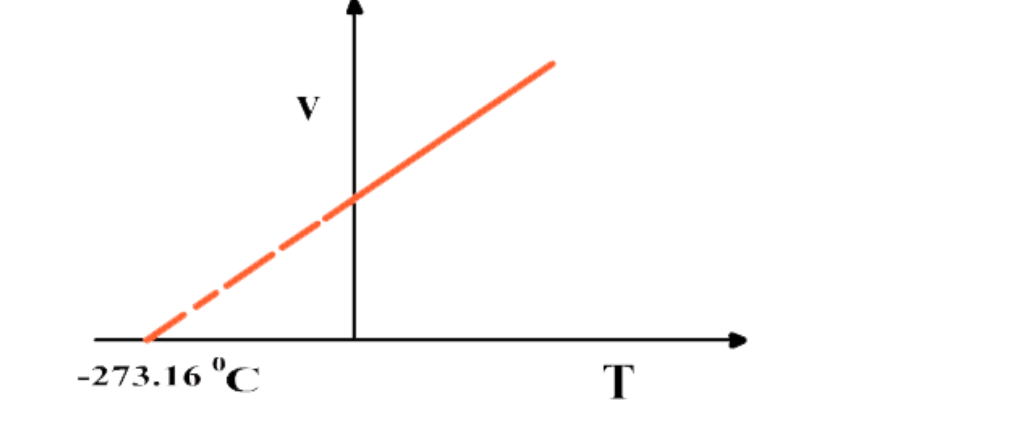
But practically volume of a gas can never become zero
Actually no gas can achieve the lowest possible temperature and before -273.16 0C all gases are condensed to liquid
This temperature is referred to as absolute scale or absolute zero
At -273.16 0C all molecular motions are ceased
This temperature is called Absolute Zero
Degrees on this scale are called Kelvin’s and are denoted by K while θ stands for a Celsius scale temperature
They are exactly the same size as Celsius degrees
Since –273 0C = 0K, conversions from 0C to K are made by adding 273 T = 273 + θ
0 0C = 273K
15 0C = 273 + 15 = 288K
The letter T represents Kelvin or absolute temperatures and θ stands for a Celsius scale temperature
Pressure law
The pressure of a fixed mass of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature if the volume is kept constant
p ∝ T or p = constant X T
Or p/T = Constant
The three equations can be combined giving
Pv = constant
T For cases in which p, V and T all change from say p1, V1 and T1 to p2, V2 and T2, then P1V1 = p2V2 T1 T2
Gases and the Kinetic Theory
2024 FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION RESOURCES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 OPENER , MID AND END TERM EXAMS
1995-2024 KCSE KNEC PAPERS QUESTIONS,ANSWERS AND REPORT
2008-2024 KCSE FORM 4 COUNTY MOCKS
FORM 1 2 3 4 SCHEMES OF WORK
FORM 1 2 3 4 LESSON PLANS
FORM 1 2 3 4 CLASS REVISION NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 HOLIDAY ASSISNMENTS
FORM 3 4 SETBOOKS STUDY GUIDES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TOPICAL TESTS
FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION BOOKLETS
LIFE SKILLS NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 SYLLABUS
KENYA SCHOOL CODES
HOW TO REVISE AND PASS EXAMS
GUIDANCE AND CONSELLING NOTES
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD ALL LATEST 2024 KCSE REVISION MOCKS
KCSE COUNTY MOCKS DOWNLOADS 2024
2023 KCSE COUNTY MOCKS DOWNLOADS
- 2023 KAPSABET BOYS POST MOCK
- PANGANI MOCK KCSE 2023
- KCSE 2023 LAINAKU II FORM 4 JOINT MOCK
- KENYA HIGH POST MOCK
- KALA MOCK =Password is- subjectcodeKALA2023
- KCSE 2023 SAMIA JOINT MOCK
LANJET 2023 EVALUATION MOCK
2023 EVALUATION MOCK nyandarua trial 4
2023 EVALUATION MOCK nyandarua trial 3
KCSE 2023 MOCKS NYARIRA CLUSTER EXAMS
KCSE 2023 CEKANA MOCKS
KCSE 2023 ACHIEVERS JOINT MOCK
- KAPSABET 2 MOCK 2023
- MOKASA 2 MOCK 2023
- 2023 Mang’u high revision mock
- FORM 4 TERM 2 BAKALE EXAM
CATHOLIC DIOCESE OF KAKAMEGA MOCK
- BSJE JOINT MOCK EXAM 2023
- MARANDA HIGH SCHOOL MOCK JUNE
- KCSE 2023 mock Nginda girls
- 2023 Kcse mock Wahundura
- 2023 Kcse mock set 22
KCSE 2023 KASSU MOCK EXAMS
- 2023 KCSE EAGLE TRIAL 1 MOCK
- 2023 lainaku revision mock
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 18
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 17
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 16
LUGARI CONSTITUENCY -MOCK 1
- 2023 KCSE FORM 4 EVALUATION TEST
2023 mokasa mocks revision exams
- SUKELLEMO JOINT PRE-MOCK EXAMS
- Mumias west pre mock kcse exams
- 2023 SUNRISE PRE-MOCK
- 2023 kcse arise and shine pre-mock
- MECS CLUSTER JOINT MOCK EXAM
- Chogoria murugi zone pre-mock
- MOMALICHE 2 EXAMS PRE MOCK
- ASUMBI PRE MOCK EXAMS 2023
- 2023 MARANDA HIGH PRE-MOCK
- KAPSABET INTERNAL TRIAL 1 2023
- FORM 4 EVALUATION TEST 2023
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams
Mock exams and pre-mock exams are practice tests that are taken before the actual exams.
2022 COUNTY MOCKS 38 EXAMS
2021-22 COUNTY MOCKS 36 EXAMS
2020-21 COUNTY MOCKS 24 EXAMS
2019 COUNTY MOCKS 44 EXAMS
2018 COUNTY MOCKS 23 COUNTIES EXAMS
2017 COUNTY MOCKS 25 COUNTIES EXAMS
2016 COUNTY MOCKS 16 COUNTIES
2015 COUNTY MOCKS 20 COUNTIES
2008 , 2009 , 2010 , 2011 , 2012 , 2013, 2014 COUNTY MOCKS 25 COUNTIES
2023 KCSE COUNTY MOCKS Mock exams and pre-mock exams are practice tests that are taken before the actual exams.
They are designed to help students get a sense of what to expect in the real exam and to identify areas where they need to improve.
The purpose of taking mock exams is to help students build confidence, develop test-taking strategies, and identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Pre-mock exams are usually taken a few weeks or months before the actual exam, while mock exams are usually taken closer to the exam date.
 WhatsApp us Now
WhatsApp us Now