Chemistry Notes Form 3
Chemistry Notes Form 3
Gas Laws
Kinetic Particle Theory
- Matter is made up of particles that are in constant motion
- The higher the temperature, the faster the particles move (more energy)
- Increase in temperature increase weakens interparticle forces, causing particles to spread apart and increase in volume/size (i.e. Expansion)
- Gases have greatest average energy while solids have smallest average energyAccording to the kinetic theory, matter is made up of particles (atoms, molecules or ions) which are in constant motion because they have energy at all temperatures above zero Kelvin (absolute zero, 0K) or -2730C.This energy is in the form of kinetic energy.
Consider heating a solid;
When a solid is heated, the particles vibrate more strongly as they gain kinetic energy and the particle attractive forces are weakened.
Eventually, at the melting point, the attractive forces are too weak to hold the particles in the structure together in an ordered way and so the solid melts.
The particles become free to move around and lose their ordered arrangement.
Energy is needed to overcome the attractive forces and give the particles increased kinetic energy of vibration.
On heating further, the particles gain more kinetic energy and move faster.
In evaporation and boiling the particles with the highest kinetic energy can ‘escape’ from the attractive forces of the other liquid particles.
The particles lose any order and become completely free to form a gas or vapour.
Boiling is rapid evaporation anywhere in the bulk liquid and at a fixed temperature called the boiling point and requires continuous addition of heat.
Diffusion and Kinetic Energy
The natural rapid and random movement of the particles means that gases readily ‘spread’ or diffuse
Diffusion is the movement of gas or solid particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
Diffusion is fastest in gases where there is more space for them to move
The rate of diffusion increases with increase in temperature as the particles gain kinetic energy and move faster
Diffusion of Ammonia and Hydrogen Chloride
The following experiment is set up
One filter soaked in a solution of ammonia solution and the other soaked in a solution of concentrated hydrochloric acid are placed on the end of along glass tubing as shown

When colourless NH3 and HCl fumes meet, dense white smoke (fumes) of ammonium chloride are observedNH3 (ag) + HCl (ag) -> NH4 Cl(s)
Ammonia is diffused more rapidly than the hydrogen chloride because the gas traveled a longer distance in the same amount of time
Gases with greater R.M.M have higher densities than gases which have small molecules eg. hydrogen chloride are heavier than ammonia molecules
If the concentration of hydrochloric acid and that of ammonia were increased in a separate experiment, the rate of diffusion would be faster
Gas Mr
NH3 17
HCl 35
5 Large heavy molecules move more slowly than small, light molecules
Therefore, dense gases diffuse more slowly than gases of low density
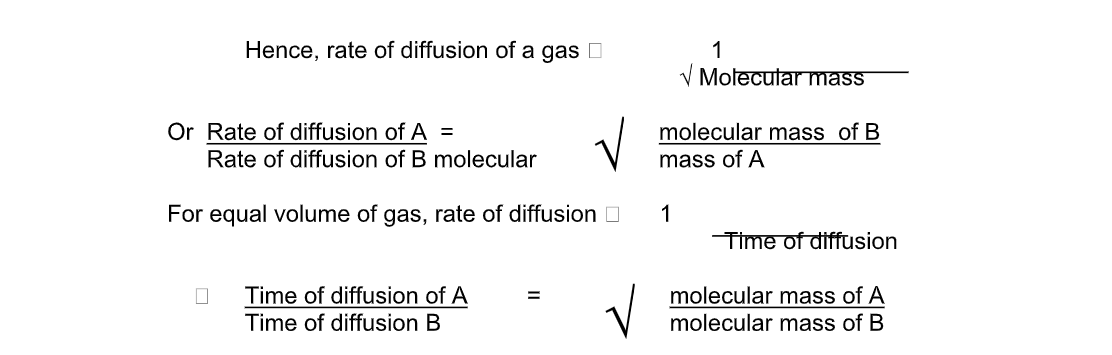
The rate of diffusion depends on the molecular mass/density of gas
Rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to mass of a gas
Rate of Diffusion;
- Increases with temperature
- Decreases with increasing R.M.M or R.A.M
- Increases with concentrationGraham’s Law of DiffusionGraham’s law of diffusion relates the rate of diffusion of a gas to its density
It states that the rate of diffusion of a gas at constant temperature and pressure is inversely proportional to the square root of its density


Evaporation, boiling and kinetic theoryOn heating particles gain kinetic energy and move faster
In evaporation and boiling the highest kinetic energy molecules can ‘escape’ from the attractive forces of the other liquid particles
The particles lose any order and become completely free to form a gas or vapour
Energy is needed to overcome the attractive forces in the liquid and is taken in from the surroundings
This means heat is taken in, so evaporation or boiling are endothermic (require energy input) processes
If the temperature is high enough boiling takes place
Boiling is rapid evaporation anywhere in the bulk liquid and at a fixed temperature called the boiling point and requires continuous addition of heat
The rate of boiling is limited by the rate of heat transfer into the liquid
Evaporation takes place more slowly at any temperature between the melting point and boiling point, and only from the surface, and results in the liquid becoming cooler due to loss of higher kinetic energy particles
2024 FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION RESOURCES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 OPENER , MID AND END TERM EXAMS
1995-2024 KCSE KNEC PAPERS QUESTIONS,ANSWERS AND REPORT
2008-2024 KCSE FORM 4 COUNTY MOCKS
FORM 1 2 3 4 SCHEMES OF WORK
FORM 1 2 3 4 LESSON PLANS
FORM 1 2 3 4 CLASS REVISION NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 HOLIDAY ASSISNMENTS
FORM 3 4 SETBOOKS STUDY GUIDES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TOPICAL TESTS
FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION BOOKLETS
LIFE SKILLS NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 SYLLABUS
KENYA SCHOOL CODES
HOW TO REVISE AND PASS EXAMS
GUIDANCE AND CONSELLING NOTES
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD ALL LATEST 2024 KCSE REVISION MOCKS
KCSE COUNTY MOCKS DOWNLOADS 2024
2023 KCSE COUNTY MOCKS DOWNLOADS
- 2023 KAPSABET BOYS POST MOCK
- PANGANI MOCK KCSE 2023
- KCSE 2023 LAINAKU II FORM 4 JOINT MOCK
- KENYA HIGH POST MOCK
- KALA MOCK =Password is- subjectcodeKALA2023
- KCSE 2023 SAMIA JOINT MOCK
LANJET 2023 EVALUATION MOCK
2023 EVALUATION MOCK nyandarua trial 4
2023 EVALUATION MOCK nyandarua trial 3
KCSE 2023 MOCKS NYARIRA CLUSTER EXAMS
KCSE 2023 CEKANA MOCKS
KCSE 2023 ACHIEVERS JOINT MOCK
- KAPSABET 2 MOCK 2023
- MOKASA 2 MOCK 2023
- 2023 Mang’u high revision mock
- FORM 4 TERM 2 BAKALE EXAM
CATHOLIC DIOCESE OF KAKAMEGA MOCK
- BSJE JOINT MOCK EXAM 2023
- MARANDA HIGH SCHOOL MOCK JUNE
- KCSE 2023 mock Nginda girls
- 2023 Kcse mock Wahundura
- 2023 Kcse mock set 22
KCSE 2023 KASSU MOCK EXAMS
- 2023 KCSE EAGLE TRIAL 1 MOCK
- 2023 lainaku revision mock
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 18
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 17
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 16
LUGARI CONSTITUENCY -MOCK 1
- 2023 KCSE FORM 4 EVALUATION TEST
2023 mokasa mocks revision exams
- SUKELLEMO JOINT PRE-MOCK EXAMS
- Mumias west pre mock kcse exams
- 2023 SUNRISE PRE-MOCK
- 2023 kcse arise and shine pre-mock
- MECS CLUSTER JOINT MOCK EXAM
- Chogoria murugi zone pre-mock
- MOMALICHE 2 EXAMS PRE MOCK
- ASUMBI PRE MOCK EXAMS 2023
- 2023 MARANDA HIGH PRE-MOCK
- KAPSABET INTERNAL TRIAL 1 2023
- FORM 4 EVALUATION TEST 2023
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams
Mock exams and pre-mock exams are practice tests that are taken before the actual exams.
2022 COUNTY MOCKS 38 EXAMS
2021-22 COUNTY MOCKS 36 EXAMS
2020-21 COUNTY MOCKS 24 EXAMS
2019 COUNTY MOCKS 44 EXAMS
2018 COUNTY MOCKS 23 COUNTIES EXAMS
2017 COUNTY MOCKS 25 COUNTIES EXAMS
2016 COUNTY MOCKS 16 COUNTIES
2015 COUNTY MOCKS 20 COUNTIES
2008 , 2009 , 2010 , 2011 , 2012 , 2013, 2014 COUNTY MOCKS 25 COUNTIES
2023 KCSE COUNTY MOCKS Mock exams and pre-mock exams are practice tests that are taken before the actual exams.
They are designed to help students get a sense of what to expect in the real exam and to identify areas where they need to improve.
The purpose of taking mock exams is to help students build confidence, develop test-taking strategies, and identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Pre-mock exams are usually taken a few weeks or months before the actual exam, while mock exams are usually taken closer to the exam date.

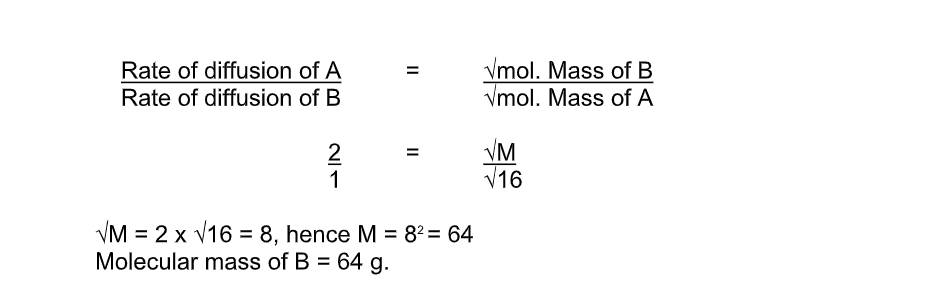
 WhatsApp us Now
WhatsApp us Now