Chemistry Notes Form 2
Chemistry Notes Form 2
Chemistry
Form 2
The Structure of the Atom and the Periodic Table
1.1 The structure of the atom
When scientists started exploring matter, they realised that matter can be divided into smaller and still smaller particles.
They called the smallest particle an ‘atom’.
The name ‘atom’ was derived from the Greek word ‘atomos’, meaning ‘indivisible’.
They discovered that the ‘atom’ maintains its chemical identity through all chemical and physical changes.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
John Dalton provided a simple theory of matter to provide theoretical justification to the laws of chemical combinations in 1805. The basic postulates of the theory are:
- All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms.
- Atoms of the same element are identical in shape, size, mass and other properties.
- Each element is composed of its own kind of atoms. Atoms of different elements are different in all respects.
- Atom is the smallest unit that takes part in chemical combinations.
- Atoms combine with each other in simple whole number ratios to form compound atoms called molecules.
- Atoms cannot be created, divided or destroyed during any chemical or physical change.Nature of AtomAt present we know that the atom is the smallest particle of an element.
It is made up of sub-atomic particles like electrons, protons and neutrons.
Atoms of one type of element differ from those of the other due to different number of sub-atomic particles.
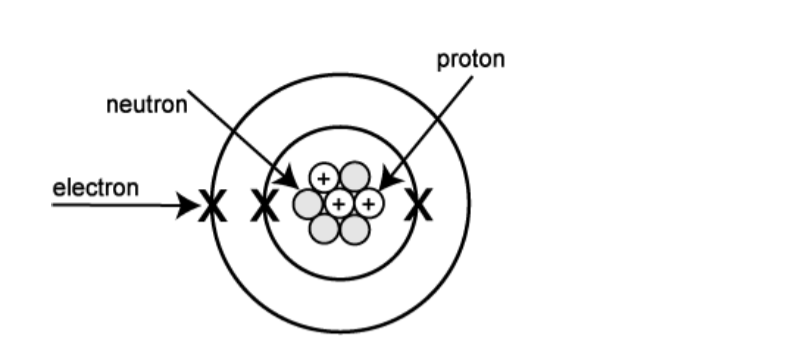
The protons and neutrons are in the nucleus (centre) of the atom and the electrons orbit round the outside in shells (energy levels or layers).
The picture below represents an atom of lithium. Lithium has 3proton, 4 neutrons and 3 electrons as shown.
Notice that the number of electrons and that of electrons are always equal in neutral atoms.

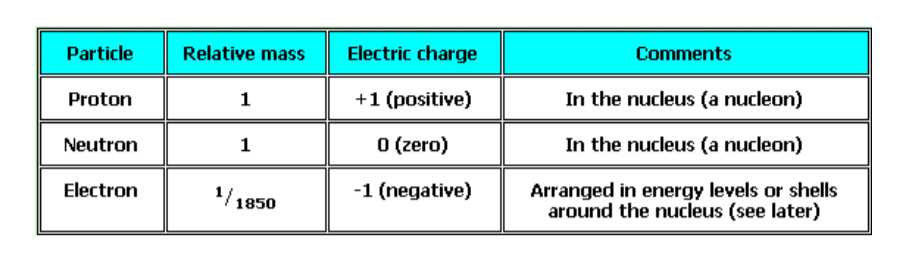
Properties of sub-atomic particles1. Electrons,
- Move around the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels
- Are negatively charged (-1)
- Have negligible mass
- Are equal to the number of neutrons in neutral atom
- Are lost or gained in chemical reactions2. Protons,
- Are present in the nucleus
- Have a positive charge (+1)
- Have a relative mass of 1 and contribute to the mass number(A) of an atom
- Are equal to the number of electrons if an atom is neutral
- Do not get lost or gained during chemical reactions
- Are equal to the atomic number(Z) of an element3. Neutrons,
- Are present in the nucleus of all atoms, except hydrogen
- Have no charge, i.e. they are electrically neutral
- Have relative mass of 1, equal to protons
- Do not get involved in chemical reactionsSummary of sub-atomic particles

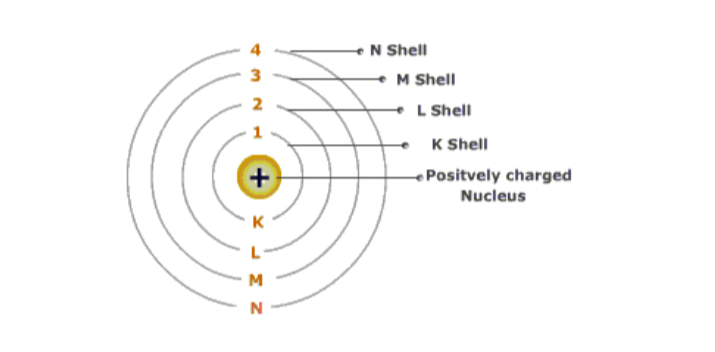
Electron energy levels in atomsThe electrons revolve rapidly around the nucleus in fixed circular paths called energy levels or shells.
The ‘energy levels’ or ‘shells’ or ‘orbits’ are represented in two ways: either by the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 or by letters K, L, M, N, O and P.
The energy of the K shell is the least while those of L, M, N and O shells increases progressively. The energy levels are counted from centre outwards.

1st energy level is K shell. It has a maximum of 2 electrons2nd energy level is L shell. It has a maximum of 8 electrons
3rd energy level is M shell. has a maximum of 8 electrons
4th energy level is N shell and so on. The 19th and 20th electrons go into the 4th shell
Electronic configuration of an element
The arrangement of electrons in the various shells/orbits/energy levels of an atom of the element is known as electronic configuration.
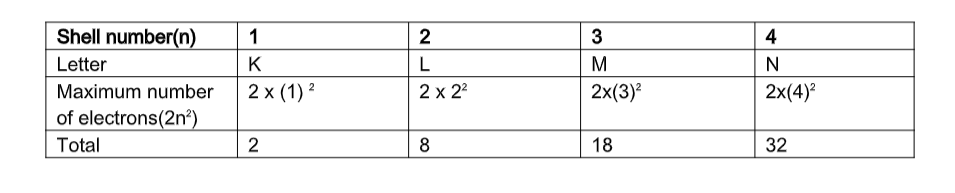
Important Rules: Number of electrons in a shell
- Maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell is given by 2n2 where n = shell number
- For 1st energy level, n = 1Maximum number of electrons in 1st energy level = 2n22 x (1) 2 = 2
- For 2nd energy level n=2Maximum number of electrons in the 2nd energy level = 2n22 x 22 = 2 x 4 = 8
- For 3rd energy level n=3Maximum number of electrons in the 3rd energy level = 2n2= 2x (3)2
= 2×9=18
- For 4th energy level n=4Maximum number of electrons in the 4th energy level = 2n2= 2x (4)2
= 2×16=32
Shell number(n) 1 2 3 4
Letter K L M N
Maximum number of electrons(2n2) 2 x (1) 2
2 x 22 2x(3)2 2x(4)2 Total 2 8 18 32

The outermost shell of an atom cannot accommodate more than 8 electrons, even if it has a capacity to accommodate more electrons.This is a very important rule and is also called the Octet rule.
The presence of 8 electrons in the outermost shell makes the atom very stable.
Geometric Representation of Atomic Structure
2024 FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION RESOURCES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 OPENER , MID AND END TERM EXAMS
1995-2024 KCSE KNEC PAPERS QUESTIONS,ANSWERS AND REPORT
2008-2024 KCSE FORM 4 COUNTY MOCKS
FORM 1 2 3 4 SCHEMES OF WORK
FORM 1 2 3 4 LESSON PLANS
FORM 1 2 3 4 CLASS REVISION NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 HOLIDAY ASSISNMENTS
FORM 3 4 SETBOOKS STUDY GUIDES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TOPICAL TESTS
FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION BOOKLETS
LIFE SKILLS NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 SYLLABUS
KENYA SCHOOL CODES
HOW TO REVISE AND PASS EXAMS
GUIDANCE AND CONSELLING NOTES
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD ALL LATEST 2024 KCSE REVISION MOCKS
KCSE COUNTY MOCKS DOWNLOADS 2024
2023 KCSE COUNTY MOCKS DOWNLOADS
- 2023 KAPSABET BOYS POST MOCK
- PANGANI MOCK KCSE 2023
- KCSE 2023 LAINAKU II FORM 4 JOINT MOCK
- KENYA HIGH POST MOCK
- KALA MOCK =Password is- subjectcodeKALA2023
- KCSE 2023 SAMIA JOINT MOCK
LANJET 2023 EVALUATION MOCK
2023 EVALUATION MOCK nyandarua trial 4
2023 EVALUATION MOCK nyandarua trial 3
KCSE 2023 MOCKS NYARIRA CLUSTER EXAMS
KCSE 2023 CEKANA MOCKS
KCSE 2023 ACHIEVERS JOINT MOCK
- KAPSABET 2 MOCK 2023
- MOKASA 2 MOCK 2023
- 2023 Mang’u high revision mock
- FORM 4 TERM 2 BAKALE EXAM
CATHOLIC DIOCESE OF KAKAMEGA MOCK
- BSJE JOINT MOCK EXAM 2023
- MARANDA HIGH SCHOOL MOCK JUNE
- KCSE 2023 mock Nginda girls
- 2023 Kcse mock Wahundura
- 2023 Kcse mock set 22
KCSE 2023 KASSU MOCK EXAMS
- 2023 KCSE EAGLE TRIAL 1 MOCK
- 2023 lainaku revision mock
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 18
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 17
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams set 16
LUGARI CONSTITUENCY -MOCK 1
- 2023 KCSE FORM 4 EVALUATION TEST
2023 mokasa mocks revision exams
- SUKELLEMO JOINT PRE-MOCK EXAMS
- Mumias west pre mock kcse exams
- 2023 SUNRISE PRE-MOCK
- 2023 kcse arise and shine pre-mock
- MECS CLUSTER JOINT MOCK EXAM
- Chogoria murugi zone pre-mock
- MOMALICHE 2 EXAMS PRE MOCK
- ASUMBI PRE MOCK EXAMS 2023
- 2023 MARANDA HIGH PRE-MOCK
- KAPSABET INTERNAL TRIAL 1 2023
- FORM 4 EVALUATION TEST 2023
- 2023 FORM 4 evaluation exams
Mock exams and pre-mock exams are practice tests that are taken before the actual exams.
2022 COUNTY MOCKS 38 EXAMS
2021-22 COUNTY MOCKS 36 EXAMS
2020-21 COUNTY MOCKS 24 EXAMS
2019 COUNTY MOCKS 44 EXAMS
2018 COUNTY MOCKS 23 COUNTIES EXAMS
2017 COUNTY MOCKS 25 COUNTIES EXAMS
2016 COUNTY MOCKS 16 COUNTIES
2015 COUNTY MOCKS 20 COUNTIES
2008 , 2009 , 2010 , 2011 , 2012 , 2013, 2014 COUNTY MOCKS 25 COUNTIES
2023 KCSE COUNTY MOCKS Mock exams and pre-mock exams are practice tests that are taken before the actual exams.
They are designed to help students get a sense of what to expect in the real exam and to identify areas where they need to improve.
The purpose of taking mock exams is to help students build confidence, develop test-taking strategies, and identify their strengths and weaknesses.
Pre-mock exams are usually taken a few weeks or months before the actual exam, while mock exams are usually taken closer to the exam date.
 WhatsApp us Now
WhatsApp us Now