Form 4 Agriculture Notes
Form 4 Agriculture Notes
K.C.S.E (Online Revision)
Livestock Production V (Poultry)
Introduction
- Poultry industry in Kenya has developed tremendously due to the use of artificial incubation and brooding and easy availability of hybrid birds, both layers and broilers.
- Poultry production has become an easy source of income and food for the rural as well as the urban communities.
- The term poultry includes domestic birds such as turkeys, ducks, geese, pheasants, doves and pigeons.
- Of late ostrich farming has become a lucrative activity.
- Poultry production starts with incubation of eggs.Parts of an Egg

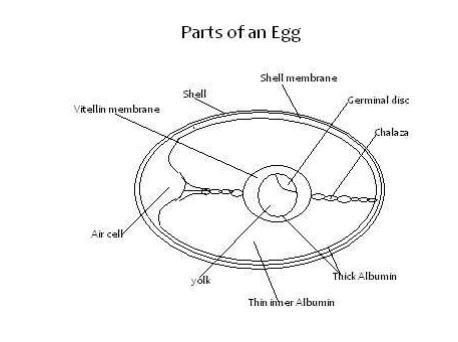
Parts of an Egg
- Shell> Forms 10-12% of the whole egg content.> Made of calcium and phosphorus.> Protects the inner egg contents.
- Shell membrane> Made of inner and outer membranes.> Lining of the egg shell.> Constitutes 1 % of the total egg content.
- Albumen (egg white)> About 55-60% of the total egg content.> It is divided into chalaza, thick and thin albumen.> Chalaza holds the egg yolk in position.> Albumen serves as food for the chick.
- Yolk> 30-33% of the total egg content.> Supply embryo with nutrients.
- Germinal disc -The embryo which develops into a chick if fertilized.
- Vitelline membrane – Gives the yolk its round shape.
- Air sac> Keeps the egg fresh by allowing gaseous exchange.> Provides oxygen for the embryoEgg Candling:
- This is the practice of determining the internal qualities of an egg by examining it against a light source.Procedure
- The egg is placed on a hole made on a cardboard box.
- This is called a candling box.
- A source of light is placed in the box directly under the egg.
- The observer then looks through the egg against the source of light below.
- Abnormalities on and within the egg can be seen through the translucent shell. incubation
- Involves the provision of fertile eggs with the proper condition for embryonic development.Selection of Eggs for incubation
- Should be fertile.
- Should be of medium size about 55- 6ogms in weight.
- Should have smooth shell.
- Should be oval shaped.
- Should not be cracked.
- Eggs should be clean to ensure that pores are open.
- Should not have abnormalities such as blood spots, meat spots and double yolk.
- Eggs should not be more than 5 days old.
- Eggs should be fresh that is collected within one week. internal egg qualities can be determined through the egg candling process.Methods of incubationNatural Incubation
- This involves the use of a broody hen which sits on the eggs to provide them with conditions necessary for hatching.
- Takes 20-21 days.
- The hen is given about 10-15 eggs.Signs of Broodiness in Poultry
- Tendency to sit on an egg after laying.
- Moulting of the hen.
- Making some noise at the laying nests.
- Feathers are raised.
- It becomes aggressive when disturbed.
- It stops laying.Preparation and Management of Natural lncubation
2024 FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION RESOURCES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 OPENER , MID AND END TERM EXAMS
1995-2024 KCSE KNEC PAPERS QUESTIONS,ANSWERS AND REPORT
2008-2024 KCSE FORM 4 COUNTY MOCKS
FORM 1 2 3 4 SCHEMES OF WORK
FORM 1 2 3 4 LESSON PLANS
FORM 1 2 3 4 CLASS REVISION NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 HOLIDAY ASSISNMENTS
FORM 3 4 SETBOOKS STUDY GUIDES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TOPICAL TESTS
FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION BOOKLETS
LIFE SKILLS NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 SYLLABUS
KENYA SCHOOL CODES
HOW TO REVISE AND PASS EXAMS
GUIDANCE AND CONSELLING NOTES
- The hen is given “China eggs” to sit on to induce broodiness.
- When broody the hen should be provided with a nesting nest or a saucershaped nest scooped on the ground.
- The nest shall be lined with soft bedding and fertile eggs provided.
- The eggs are set in the evening or night.
- The bird is dusted to control externa parasites.
- The hen is allowed t hour outside to feed and exercise everyday.
- Broken eggs should be removed immediately.
- The hen s ould not be disturbed.Advantages of Natural Incubation
- It is cheap.
- High hatchability.
- Low risk involved.
- Useful in small scale production.
- Less skill is required.
- Less laborious.Disadvantages of Natural Incubation
- Egg production is low because the hen will not lay eggs during incubation.
- It is not possible to plan when to incubate.
- If the hen dies the eggs will be destroyed.
- If the hen deserts the eggs or refuses to sit on them the farmer will incur losses.
- Only few chicks can be atched at a time by one hen.
- Diseases and parasites could easily be transmitted to the chicks.Artificial Incubation
 WhatsApp us Now
WhatsApp us Now