Form 3 Agriculture Notes
Form 3 Agriculture Notes
Form 3
Notes
Livestock Production III
(Selection and Breeding)
Introduction
- The breeding of animals is under human control, and the breeders decide which individuals shall produce the next generation.
- The breeder makes a choice.
- The breeding of animals is based upon the fact that certain qualities are genetic ,hence valuable qualities are passed on from parents to off -springs.
- The qualities can be maintained or improved in the next generation.The performance of an animal is influenced by two major factors;
- Genetic potential
- The environment, which includes:◦ Feeding,◦ Health,
◦ Care
◦ The ecological conditions.
- The genetic potential of an animal is inherited from its parents.
- In selection and breeding animals with superior characteristics are selected and allowed to mate.
- In the process they transmit the superior characteristics to their offspring.
- When this is done over a long period of time, it results in livestock improvement.Reproduction and Reproductive Systems
- Reproduction is the process by which off-springs are produced.
- All farm animals multiply by means of sexual reproduction.
- It begins with fertilization which is the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
- Fertilization takes place internally in the body of the female.
- The embryo(zygote) formed develops inside body of mother, fed and protected until end of gestation period.
- In poultry, the process is different in that eggs are fertilized internally but laid and development of the chick takes place outside during incubation.
- In both male and female, certain organs are specialized for the process of reproduction.
- Some of these organs secret fluids which are necessary for the movement and survival of the gametes(reproductive cells.)Reproduction in Cattle
- The male reproductive organs produce the male gametes,the spermatozoans.
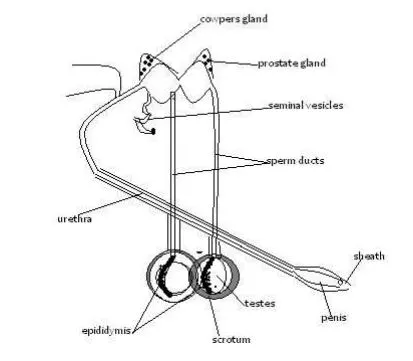
- These are introduced into female reproductive system, where they fuse with the sperm to form zygote.Reproductive system of a bull

- The testis:> There are two testes hanging loosely between hind legs.> Enclosed by loose skin (scrotum)scrotum regulate temperature of testis for optimum production of sperms.
> Produce spermatozoa(sperms)which are stored in coiled tube called epididymis
- Epididymis: Storage of spermatozoa.
- Sperm ducts:> Conveys sperm from the testis and urine through the penis.> sphincter muscles contract to allow each to pass separetly.
- Seminal vesicles produce fluid called semem.
- semen carries sperms out of penis in fluid form.
- Prostate gland -produce fluid that neutralize the acidic effects of urine in the urethra preventing death of sperms.
- Accessory glands: Include seminal vesicles cowpers gland and prostate gland.
- Urethra: Conveys urine and semen.
- Penis:> Surrounded by a sheath which is an extension of skin.> It introduces sperms into the vagina of a cow through the vulva during mating
> It is a copulatory organ, also used for urination.
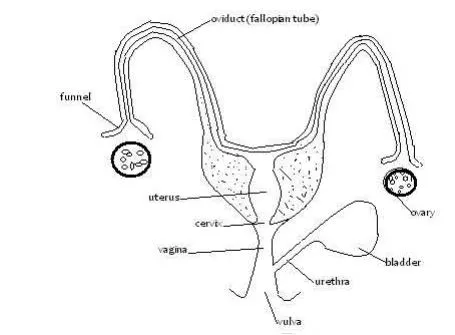
Reproductive system of a cow

Ovaries and fallopian tubes(oviduct)
- Two ovaries located in abdomen, left and right.
- Produce ova/e%gs and hormones which control sexual cycle.
- Oestrogen produced by graafian follicle inside ovary induces oestrus ie. Heat period so that the cow shows signs of heat
- After every 21 days the ovary releases a mature ovum and the cow comes on heat.
- The ovum travels through the fallopian tubes to the uterus.
- The release and movement of the ovum down to the uterus is called ovulation.
- If mating is done at this time, fertilization will take place.
- The fertilized egg implants itself onto the endometrium(walls of uterus)and develops into foetus.Fallopian tubes:
2024 FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION RESOURCES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 OPENER , MID AND END TERM EXAMS
1995-2024 KCSE KNEC PAPERS QUESTIONS,ANSWERS AND REPORT
2008-2024 KCSE FORM 4 COUNTY MOCKS
FORM 1 2 3 4 SCHEMES OF WORK
FORM 1 2 3 4 LESSON PLANS
FORM 1 2 3 4 CLASS REVISION NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TERM 1 2 3 HOLIDAY ASSISNMENTS
FORM 3 4 SETBOOKS STUDY GUIDES
FORM 1 2 3 4 TOPICAL TESTS
FORM 1 2 3 4 REVISION BOOKLETS
LIFE SKILLS NOTES
FORM 1 2 3 4 SYLLABUS
KENYA SCHOOL CODES
HOW TO REVISE AND PASS EXAMS
GUIDANCE AND CONSELLING NOTES
- Fertilization takes place here.
- Also a passage for the egg from the ovary to the uterus.The uterus:
- Embryo develops here.The cervix: Closes the uterus.The vagina and Vulva:
- Vulva is the external opening of female reproductive system.
- It allows mating to take place so that sperms are deposited into the vagina.
- The foetus and urine are removed through the vulva.Pregnancy
- Is period between fertilization of ova and the expulsion of the foetus through the vulva.
- Also called gestation period.
- In cattle gestation period is 270-285 days.
- Ends with the birth of a calf.
- The reproductive tract undergoes a period of rest during which it is repaired and returns to normal.
- During pregnancy, hormone called progesterone is produced by the placenta to maintain the foetus in the uterus.Parturition(giving birth)
- Act of giving birth called parturition.
- This time the foetus expelled through the birth canal.When an animal is about to give birth, it shows sign;> Distended udder which produces thick milky fluid called colostrums.
> Swollen vulva producing thick mucus.
> Loose and slackened pelvic girdle.
> Visible pin bones.
> General restlessness.
- Animal parturates within 2-3 hours after this signs.
- The correct presentation is with the front feet first ,and the head outstretched and resting in between the fee.
- Any other presentation called mal-presentation or breech presentation and requires assistance.Reproduction in Poultry
- The cock has no penis but a small opening near the vent through which sperms are emitted.
- Cock has testes within the body.
- The hen has elongated oviduct for formation of an egg.
- Fertilization occurs internally.
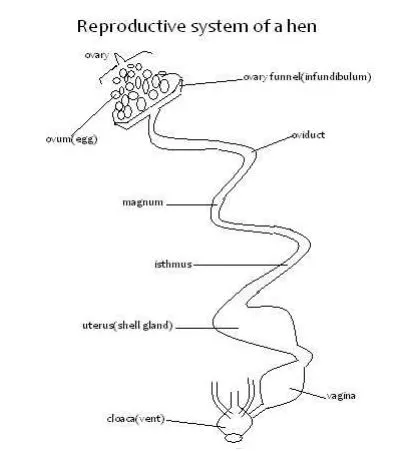
- During mating the cloaca of the hen and the vent of the cock fit into each other and then semen is poured into the cloaca ,then sucked to the oviducts.The Reproductive System of a Hen

Ovary
- Hen has two ovaries but one functional.
- Ova formed in ovaries.
- 3500-4000 ova present inside ovary held by follicle.
- Mature ovum released
- via rapture of follicle.
- It moves into oviduct received by the funnel.Funnel(infundibulum)
- Fertilization occurs here.
- Chalazae also added to yolk.
- Time here is 15 minutes.
- It is 11.6cm long.Magnum
- Thick albumen is added.
- Stays for 3hrs.its 33cmIsthmus
- Its 10.6cm long.
- Shell membranes added.
- Determines shape of egg.
- Water, mineral salts and vitamins added.
- Takes 15 minutes.Uterus(shell gland)
- Calcium deposited 9ie.
- Pigments added.
- shell added around the egg.
- Addition of albumin finished.
- Stays here for 18-22hours.Vagina
- Short, 6.9cm long.
- For temporal storage of egg before layingCloaca
- Egg moves out of cloaca through the vent.
- The cloaca extents out to prevent the egg from breaking.
 WhatsApp us Now
WhatsApp us Now